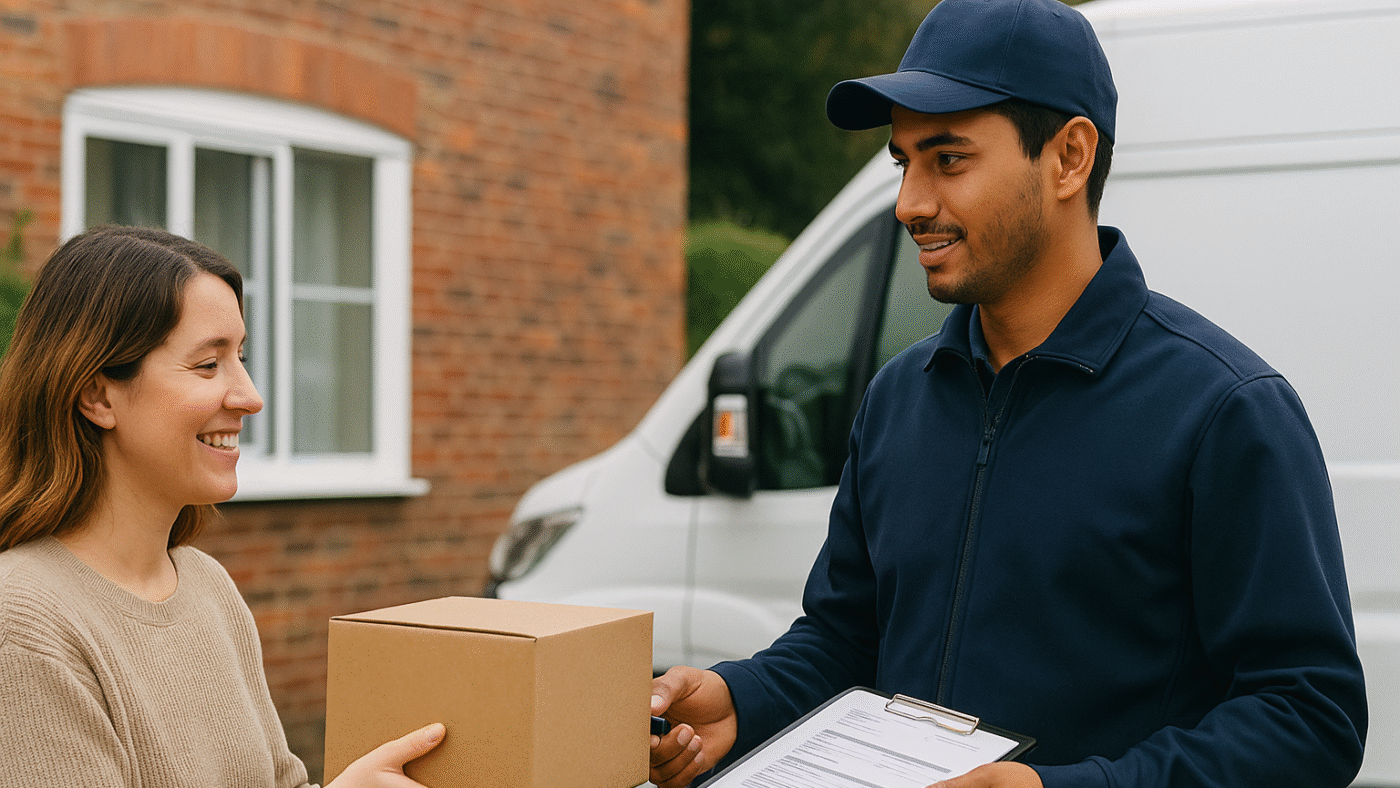
In the rapidly evolving world of e-commerce, last-mile delivery has emerged as one of the most crucial and challenging aspects of the supply chain. For India, with its diverse geography, varying infrastructure, and rapidly growing online shopping population, streamlining last-mile delivery is more than just a logistical necessity; it is a competitive differentiator.
Understanding Last-Mile Delivery in India
Last-mile delivery refers to the final step of the delivery process, where goods are transported from a warehouse or distribution center to the end consumer. This stage is often the costliest and most time-consuming part of the supply chain, accounting for up to 53% of the total shipping cost. In India, factors such as congested urban areas, remote rural locations, and inconsistent address systems amplify the complexities.
Challenges in Last-Mile Delivery
- Urban Congestion: Traffic in major cities like Mumbai, Delhi, and Bengaluru often leads to delays, increasing delivery times and costs.
- Rural Reach: A significant portion of India’s population resides in rural areas where infrastructure can be inadequate, making it difficult to ensure timely and reliable deliveries.
- Addressing Issues: Non-standardized addressing systems and landmarks being used as address references often complicate navigation for delivery personnel.
- High Delivery Costs: The fragmented nature of deliveries, especially for low-value goods, raises operational costs.
- Customer Expectations: With same-day and next-day delivery becoming the norm, customer expectations around speed and reliability are higher than ever.
Innovations and Solutions
To overcome these challenges, Indian logistics companies and e-commerce platforms are adopting innovative approaches:
- Technology Integration:
- AI and Machine Learning: Predictive analytics help optimize delivery routes, ensuring efficiency and cost savings.
- Real-time Tracking: GPS and IoT devices enable customers and companies to track deliveries in real-time, improving transparency.
- Hyperlocal Delivery Models: Partnering with local delivery agents and using gig economy workers for last-mile deliveries ensures faster service, especially in urban areas.
- Micro-warehousing: Establishing smaller warehouses closer to consumer hubs reduces the distance and time required for last-mile delivery.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): EVs are being adopted for urban deliveries, reducing both costs and environmental impact.
- Crowdsourced Delivery: Platforms are leveraging crowdsourcing models, allowing individuals to deliver packages during their routine commutes.
- Drone Deliveries: Though still in its nascent stage, drones are being piloted for faster deliveries in hard-to-reach areas.
Government Initiatives and Policies
The Indian government’s initiatives, such as the National Logistics Policy and Digital India, aim to enhance the efficiency of logistics and delivery networks. Investments in infrastructure development, coupled with regulatory support for EVs and drones, are creating a conducive environment for innovation.
The Road Ahead
The future of last-mile delivery in India is poised for transformation, driven by technology and collaboration. Companies that can balance speed, cost, and customer satisfaction will lead the charge in this competitive landscape. As rural and semi-urban areas become increasingly integrated into the e-commerce ecosystem, the focus on inclusive and efficient delivery systems will only grow.
Conclusion
Streamlining last-mile delivery in India is not just about overcoming logistical hurdles; it’s about enhancing customer experiences, reducing costs, and driving sustainability. By embracing innovation and fostering collaboration, India can set a benchmark in last-mile delivery, turning challenges into opportunities in this fast-paced digital era.